Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-10 Origin: Site











Imagine a world where rust and decay are no longer threats to metal structures. Galvanized steel panels offer this promise, providing unmatched durability and corrosion resistance. But what exactly are these panels, and why are they crucial in today's industries? In this article, you'll learn about the composition and benefits of galvanized steel panels. We'll explore their vital role in construction, automotive, and more, comparing them to alternatives like aluminum panels.
Galvanized steel is regular steel coated with a protective layer of zinc. This zinc layer shields the steel beneath from rust and corrosion caused by moisture, air, and other environmental factors. Essentially, the steel core provides strength, while the zinc coating acts as a barrier against damage.
The zinc layer can be pure zinc or a zinc alloy, often combined with iron. This combination creates a strong bond between the zinc and steel, making the coating durable and long-lasting. The coating thickness varies depending on the intended use and environmental exposure. Despite the protective layer, galvanized steel maintains the same workability as regular steel—it can be cut, drilled, and shaped as needed.
Two main methods apply the zinc coating: hot-dip galvanizing and cold galvanizing.
Hot-Dip Galvanizing: This is the most common method. Steel is dipped into molten zinc at around 460°C. The zinc bonds metallurgically with the steel, forming a tough, corrosion-resistant layer. The process creates a gradient where zinc and steel intermingle, enhancing adhesion. This method produces a thick, durable coating ideal for outdoor and industrial use.
Cold Galvanizing: This involves applying a zinc-rich paint or spray at room temperature. While it offers some corrosion protection, the coating is thinner and less durable than hot-dip galvanizing. Cold galvanizing is often used for touch-ups or smaller items that can't be hot-dipped.
Other specialized methods exist, such as sherardizing (using zinc vapor or powder) and zinc spraying, but hot-dip and cold galvanizing remain the most widely used.
Galvanized steel differs from other steel types mainly in its corrosion resistance and longevity:
| Steel Type | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Carbon Steel | Low | High | Structural components, machinery |
| Galvanized Steel | High (due to zinc) | High (steel core) | Outdoor structures, automotive |
| Stainless Steel | Very High (alloyed) | Moderate to High | Medical, food processing, marine |
| Cold-Rolled Steel | Low | Moderate | Precision parts, appliances |
Galvanized steel offers an excellent balance of strength, cost, and corrosion protection. While stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance, it is more expensive. Regular carbon steel lacks corrosion protection and rusts quickly outdoors. Galvanized steel extends lifespan significantly, especially in harsh or moist environments.
Galvanized steel panels are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance. The zinc coating acts as a strong barrier, preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the steel underneath. This protective layer significantly slows down rust formation, even in harsh environments like coastal areas or industrial zones with high pollution. Moreover, the zinc provides sacrificial protection—if the coating is scratched or damaged, the zinc around the exposed area corrodes first, safeguarding the steel beneath.
This corrosion resistance translates into outstanding durability. Galvanized panels can last anywhere from 20 to 50 years or more, depending on exposure conditions. This makes them ideal for outdoor use where long-term performance is critical. The coating also resists wear and tear from physical impacts, helping panels maintain their integrity over time.
Despite the zinc coating, galvanized steel panels retain the inherent strength of steel. They offer high tensile strength and can withstand heavy loads, making them suitable for structural applications. At the same time, these panels exhibit a degree of flexibility. This balance allows them to be cut, bent, and shaped during fabrication without compromising their protective layer. It also means they can absorb shocks and vibrations better than more brittle materials.
The combination of strength and flexibility is especially important in construction and automotive industries, where materials must endure mechanical stress while maintaining form and function.
Galvanized steel panels score well on environmental and sustainability fronts. Zinc, the primary coating material, is a naturally occurring element that is non-toxic and recyclable. The galvanization process extends the life of steel products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste.
Additionally, galvanized steel panels require little maintenance. This means fewer resources spent on repainting or repairs over their lifespan. Many galvanized steel products are also made from recycled steel, and at the end of their use, they can be fully recycled again, supporting circular economy principles.
The durability and recyclability of galvanized steel panels make them a smart choice for eco-conscious projects aiming to reduce environmental footprints. When specifying galvanized steel panels for outdoor projects, consider the zinc coating thickness to match environmental exposure, ensuring optimal corrosion resistance and longevity.
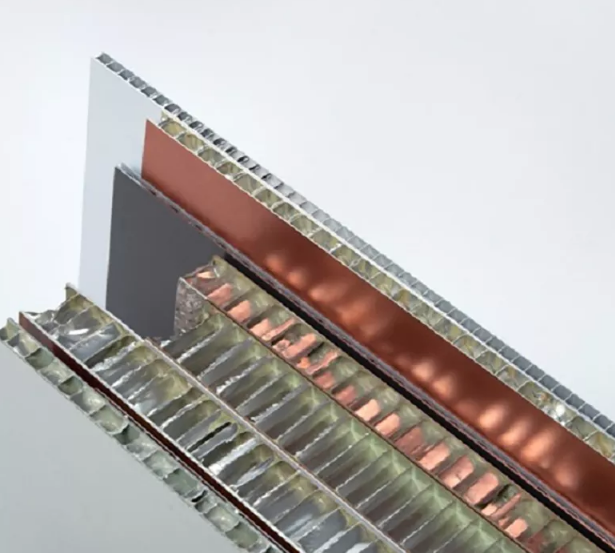
In construction, galvanized steel panels serve multiple purposes. They are commonly used for roofing and wall cladding because the zinc coating protects against rust and weather damage. This makes buildings more durable and reduces maintenance costs over time.
Structural frameworks also benefit from galvanized steel panels. Beams, columns, and trusses made from these panels can withstand heavy loads and harsh weather. Their strength and corrosion resistance ensure safety and longevity for buildings.
Additionally, galvanized steel is popular for making fences, gates, and barriers. These outdoor structures need to resist rust and physical wear, making galvanized panels an ideal choice. HVAC ductwork also often uses galvanized steel because it resists moisture and can be easily fabricated into complex shapes.
The automotive industry relies on galvanized steel panels for many vehicle parts. Body panels and frames made from galvanized steel resist rust, extending vehicle life. This is especially important in areas exposed to road salt or humid climates.
Exhaust systems and fuel tanks also use galvanized steel because it withstands high temperatures and corrosive substances. Railroads benefit too, using galvanized steel for tracks and components that endure heavy loads and exposure to elements.
Shipping containers are another key application. Galvanized steel panels protect containers from rust during long sea or land transport, ensuring goods stay safe.
Industrial settings use galvanized steel panels in building materials, machinery, and equipment enclosures. Their corrosion resistance protects electrical control panels and mechanical parts, reducing downtime and repair costs.
In agriculture, galvanized steel is used to make silos, fences, and irrigation systems. These panels resist chemicals and weather, making them perfect for farm environments. The durability of galvanized steel helps lower maintenance and replacement expenses for farmers. When selecting galvanized steel panels for outdoor or industrial projects, choose a coating thickness suited to the environment to maximize protection and lifespan.
Galvanized steel panels offer outstanding value for money. The zinc coating protects steel from rust and corrosion, which extends the panel’s lifespan significantly. In many cases, these panels last 20 to 50 years or more, depending on environmental conditions. This long service life reduces the need for frequent replacements, saving money over time.
Compared to other corrosion protection methods, galvanization is often more affordable. The initial cost of galvanized panels is balanced by lower maintenance and repair expenses. For example, unlike painted steel, galvanized panels don’t require regular repainting or touch-ups. This makes them a smart investment for projects where durability and budget are priorities.
One major advantage of galvanized steel panels is their minimal maintenance needs. The zinc layer acts as a barrier against moisture, dirt, and chemicals, preventing rust before it starts. Even if the coating gets scratched, the zinc around the damaged area corrodes first, protecting the steel beneath. This self-healing property means small damages do not lead to rapid corrosion.
Because of this, galvanized panels can be left outdoors for years without special care. They don’t need frequent cleaning, repainting, or protective treatments. This reduces labor and material costs over the panel’s life. For industrial or agricultural uses where access for maintenance is limited, this is a huge benefit.
Galvanized steel panels also provide both aesthetic and functional advantages. The zinc coating gives panels a clean, shiny, and uniform appearance that many find visually appealing. This natural metallic finish fits well in modern architectural designs and industrial settings without needing extra painting or finishing.
Functionally, galvanized panels are strong yet flexible. They can be easily cut, bent, or shaped during fabrication without cracking the protective coating. This versatility allows designers and builders to create custom shapes and sizes for various projects. The panels also resist dents and impacts better than many other materials, maintaining their look and performance longer.
Additionally, galvanized steel is compatible with other materials and finishes. It can be painted or coated again if desired, adding color options or extra protection. This adaptability makes galvanized panels suitable for a wide range of applications where both form and function matter.
Tip: When budgeting for projects, consider the long-term savings from galvanized steel panels’ durability and low maintenance, not just the upfront cost.
Galvanized steel panels are known for their impressive strength. They provide a sturdy framework, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications like construction and industrial use. Steel’s tensile strength is much higher than aluminum’s, allowing it to handle heavier loads without bending or breaking.
On the other hand, aluminum panels are much lighter. This makes aluminum a great choice when weight reduction is a priority, such as in aerospace or transportation industries where fuel efficiency matters. However, aluminum’s strength is moderate compared to steel. It can bend or dent more easily under stress.
In summary, galvanized steel offers superior strength but is heavier, while aluminum provides lightweight flexibility with less strength.
When it comes to cost, galvanized steel panels generally have a lower upfront price than aluminum. Steel is more abundant and less expensive to produce. This cost advantage makes galvanized steel panels a budget-friendly option for large projects.
Durability favors galvanized steel as well. The zinc coating on steel protects it from rust and corrosion, extending its lifespan significantly. Galvanized steel panels can last 20 to 50 years or more, depending on environmental exposure. Aluminum naturally resists corrosion due to its oxide layer, but it can suffer from surface wear and fatigue over time, especially in harsh conditions.
While aluminum requires less maintenance, its initial higher price and lower strength might offset that benefit in some uses. For long-term structural applications, galvanized steel often provides better value due to its durability and strength.
Both materials have environmental benefits. Galvanized steel panels are highly recyclable, and the zinc coating process enhances longevity, reducing waste from frequent replacements. Aluminum is also recyclable and lighter, which can reduce transportation emissions.
Usage depends on project needs. Galvanized steel panels suit applications needing high strength, such as building frameworks, roofing, and automotive parts. Aluminum panels work well where weight savings are critical, like aircraft, marine vessels, or lightweight cladding.
In some cases, choosing between galvanized steel and aluminum comes down to balancing strength, weight, cost, and environmental impact according to the project's priorities. For projects requiring high structural strength and cost efficiency, choose galvanized steel panels; for lightweight applications where corrosion resistance and ease of handling matter more, aluminum panels may be preferable.
Galvanized steel panels continue to evolve thanks to advances in coating technology. New coatings aim to boost corrosion resistance while being eco-friendly. For example, chromium-free coatings are gaining popularity because they avoid environmental hazards linked to traditional chrome treatments. These coatings still provide strong protection but without toxic effects.
Self-healing coatings are another exciting innovation. They can repair tiny scratches automatically by reacting with moisture and oxygen. This feature helps maintain the panel’s integrity without costly maintenance. Such coatings extend the lifespan and reduce downtime for repairs.
Other developments focus on improving coating thickness uniformity and adhesion. Better bonding between zinc and steel means panels resist peeling or chipping longer. Some coatings combine zinc with other metals like aluminum or magnesium for enhanced durability. These hybrid layers offer superior protection in harsh environments, such as coastal or industrial areas.
Sustainability drives much of the galvanized steel panel demand today. Builders and architects seek materials that reduce environmental impact and promote energy efficiency. Galvanized steel fits well here because it’s recyclable and lasts a long time, cutting down waste from replacements.
Green building certifications like LEED encourage using materials with low embodied energy and long service life. Galvanized steel panels meet these criteria, especially when produced with energy-efficient galvanizing methods. Their corrosion resistance reduces the need for repainting or repairs, further lowering carbon footprints.
Additionally, galvanized steel supports renewable energy projects. For instance, solar panel mounting systems often use galvanized steel for strength and weather resistance. Urban infrastructure projects also favor galvanized panels for bridges, facades, and ventilation systems due to their durability and recyclability.
The market for galvanized steel panels is poised for growth. Infrastructure investments worldwide increase demand for durable materials. Emerging economies are expanding construction sectors, creating new opportunities for galvanized steel.
Manufacturers are exploring lightweight galvanized steel alloys to improve handling and reduce transportation costs. This innovation could open doors to applications in automotive and aerospace industries where weight matters.
Digital technologies like AI and IoT also play a role. Smart coatings that monitor corrosion or wear in real-time may soon become standard. This would allow predictive maintenance, saving money and preventing failures.
Finally, stricter environmental regulations will push for greener production and recycling processes. Companies adopting sustainable practices early will gain competitive advantages. When selecting galvanized steel panels, consider new eco-friendly coatings and certifications to future-proof your projects and meet sustainability goals.
Galvanized steel panels offer exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for various applications. They provide a cost-effective solution with low maintenance needs and aesthetic appeal. These panels are strong, flexible, and environmentally friendly, supporting sustainable construction trends. As demand grows, innovations in coating technologies enhance their performance. MC BOND offers high-quality galvanized steel panels, emphasizing durability and value for diverse projects. Choose MC BOND for reliable and sustainable steel solutions.
A: Galvanized steel panels are regular steel sheets coated with a protective layer of zinc, providing corrosion resistance and durability, ideal for outdoor and industrial applications.
A: Galvanized steel panels offer superior strength and durability, while aluminum panels are lighter, making them suitable for applications where weight is a priority.
A: Galvanized steel panels are chosen for construction due to their high strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring long-lasting performance.
A: Galvanized steel panels generally have a lower upfront cost than aluminum panels, offering a budget-friendly option with extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs.
A: Galvanized steel panels can last 20 to 50 years or more, depending on environmental exposure, thanks to their protective zinc coating.